Sugar is found naturally in every food in which carbohydrates are present. Foods like various fruits, grains and dairy (lactose) have an amount of natural sugar in them. When you eat whole foods with raw sugar, there is little or no damage which can occur compared to the regular white sugar we all know. A high consumption of these foods can actually help reduce the risks of chronic heart disease, diabetes and high blood pressure. However, when an individual consumes any sugar in excess, it can cause significant threats to their health.
Insulin is a natural hormone, synthesized by the pancreas, which regulates how the body uses and stores sugar. When sugar is consumed excessively, the presence of insulin is doubled in the bloodstream, making the walls of the arteries inflamed. This makes them grow thicker than they ought to be and become less flexible, which increases the workload of the heart and may cause other afflictions such as strokes, heart attacks, heart failures and even damages to various nerves.
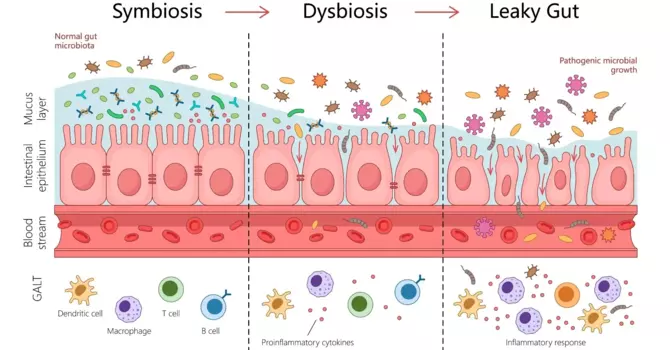
In the presence of an excess amount of sugar in the body, the body becomes susceptible to several kinds of disease. It becomes weak in fighting off toxic substances, like bacteria and viruses, as the immune system becomes compromised. Recent studies have shown that an increase in sugar consumption suppresses, or weakens, the immune system.
Frequent intake of foods rich in sugar generally reduces the body’s ability to fight off diseases. White blood cells, also known as 'killer cells', who normally help protect the body from viruses and bacteria, are weakened by excess sugar in the blood. A study was carried out and it was discovered that monocytes, a certain kind of leucocyte (white blood cells), became inflamed when cultured in fructose. It is also known that dendritic cells (antigen-presenting cells), also called accessory cells and very important in the immune system, became inflamed when exposed to excess fructose. When these cells are compromised, the body's ability to ward off disease reduces.
An excess consumption of sugar impedes the cognitive skills and self-control of an individual. Excess consumption of sweet foods produces addiction-like effects in the brain, often leading to the loss of self-control in regards to food, abnormal weight gain, and overeating. Foods rich in sugar help enhance regions of the brain responsible for reward responses and promote a heightened feeling of hunger, compared to those relatively low in sugar. Recent studies have shown that sugar can be more addictive than cocaine. A slight increase in the average sugar level of the body could have significant impacts on the brain.
An excess sugar intake causes inflammation in the brain, leading to difficulties in memory. Problems in learning, memory, motor speed, deterioration of mental capacity and other cognitive functions also occur. This is due to the damage to the tiny blood vessels present in the brain. This subsequently affects the brain's white matter (a part of the brain where nerves communicate with themselves), and can result in vascular dementia. This is why Alzheimer’s disease is often referred to as Type 3 Diabetes.
In conclusion, sugar in small amounts and from naturally occurring sources such as fruits, vegetables and whole grains can be part of a healthy diet and lifestyle. It’s when sugar is consumed in excess and particularly from processed and artificial sources that it can have life altering, detrimental effects as explained above.

Dr. Alfred Alessi
Director of Clinics, Integrative Health Practitioner, Doctor of Chiropractic
Contact Me